JS 异步编程进化史
JS 异步编程事件顺序如下:
- Callback 回调函数
- Promise 链式调用
- Generator / yield
- async / await
- 由于 JS 事件处理是异步的。在 JS 中, 事件监听会被添加到事件队列中,等待主线程处理。通常我们会将事件监听作为 JS 算入异步编程中的一种。
- 作为一种拓展模式,发布/订阅模式,是属于设计模式中的行为模式。也常常被用来做异步编程。
Callback
Callback(回调函数)本质就是被: 作为实参传入另一个函数,并在外部函数内被调用,用以来完成某些任务的函数,成为会调函数。
function greeting(name) {
alert("Hello " + name);
}
function processUserInput(callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
var name = prompt("Please enter your name.");
}, 1000);
callback(name);
}
processUserInput(greeting);
Callback Hell: 最大的问题就是使用复杂嵌套进行回调会导致,每个回调都在接受参数,该参数是上一个回调的返回。这种结构类似于一个金字塔,难以阅读和维护。
// Example of Callback Hell.
const Axios = require("axios").default;
const USERS_URL = "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users";
const POSTS_URL = "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts";
const COMMENTS_URL = "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/comments";
function getFunc(URL, cb) {
Axios.get(`${URL}`).then((response) => {
const { data } = response;
cb(data);
});
}
function getCommentByUser(username) {
getFunc(`${USERS_URL}?username=${username}`, (user) => {
getFunc(`${POSTS_URL}?userId=${user[0].id}`, (posts) => {
getFunc(`${COMMENTS_URL}?postId=${posts[0].id}`, (comments) => {
const firstComment = comments[0];
console.log(firstComment);
});
});
});
}
getCommentByUser("Samantha");
Promise
一个 Promise 是一个代理,它代表一个在创建 promise 时不一定已知的值。它允许你将处理程序与异步操作的最终成功值或失败原因关联起来。这使得异步方法可以像同步方法一样返回值:异步方法不会立即返回最终值,而是返回一个 promise,以便在将来的某个时间点提供该值。
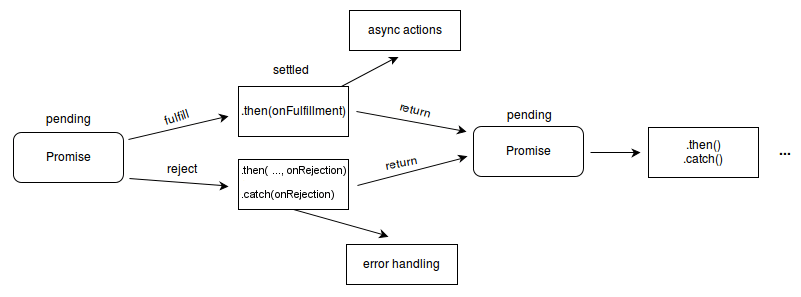
Promise 必然存在的三种状态:
- pending: 初始状态
- fulfilled: 操作完成
- rejected: 操作失败
function myAsyncFunction(url) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open("GET", url);
xhr.onload = () => resolve(xhr.responseText);
xhr.onerror = () => reject(xhr.statusText);
xhr.send();
});
}
myAsyncFunction("/xxx")
.then((res) => successFunc(res))
.catch((err) => errorFunc(err));
Promise 链式调用
myPromise
.then((value) => `${value} and bar`)
.then((value) => `${value} and bar again`)
.then((value) => `${value} and again`)
.then((value) => `${value} and again`)
.then((value) => {
console.log(value);
})
.catch((err) => {
console.error(err);
});
Generator / yield
Generator 函数(生成器函数): 它允许自定义一个非连续执行函数作为迭代算法。
最初调用时,生成器函数不执行任何代码,而是返回一种称为生成器的特殊迭代器。通过调用 next()方法消耗生成器时,生成器函数将执行,直至遇到 yield 关键字。
function* fibonacci() {
let current = 0;
let next = 1;
while (true) {
const reset = yield current;
[current, next] = [next, next + current];
if (reset) {
current = 0;
next = 1;
}
}
}
const sequence = fibonacci();
console.log(sequence.next().value); // 0
console.log(sequence.next().value); // 1
console.log(sequence.next().value); // 1
console.log(sequence.next().value); // 2
console.log(sequence.next().value); // 3
console.log(sequence.next().value); // 5
console.log(sequence.next().value); // 8
console.log(sequence.next(true).value); // 0
console.log(sequence.next().value); // 1
console.log(sequence.next().value); // 1
console.log(sequence.next().value); // 2
function* fetchUsers() {
yield fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users")
.then((resp) => resp.json())
.then((users) => {
return users;
});
}
const usersIt = fetchUsers();
usersIt.next().value.then((resp) => console.log(resp));
async / await
function resolveAfter2Seconds() {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('resolved');
}, 2000);
});
}
async function asyncCall() {
console.log('calling');
const result = await resolveAfter2Seconds();
console.log(result);
// Expected output: "resolved"
}
asyncCall();